Young Americans Study: Methodology
This Navigator Research report is the fifth and final release among 4,000 Americans under the age of 35 across five different modes to understand where they stand on issues facing the nation today. Today’s release focuses on the actual methodology of this survey, including where there are similarities and differences among young Americans based on whether they responded to our survey via live phone, online panel, text to web, or in-platform social media recruitment.
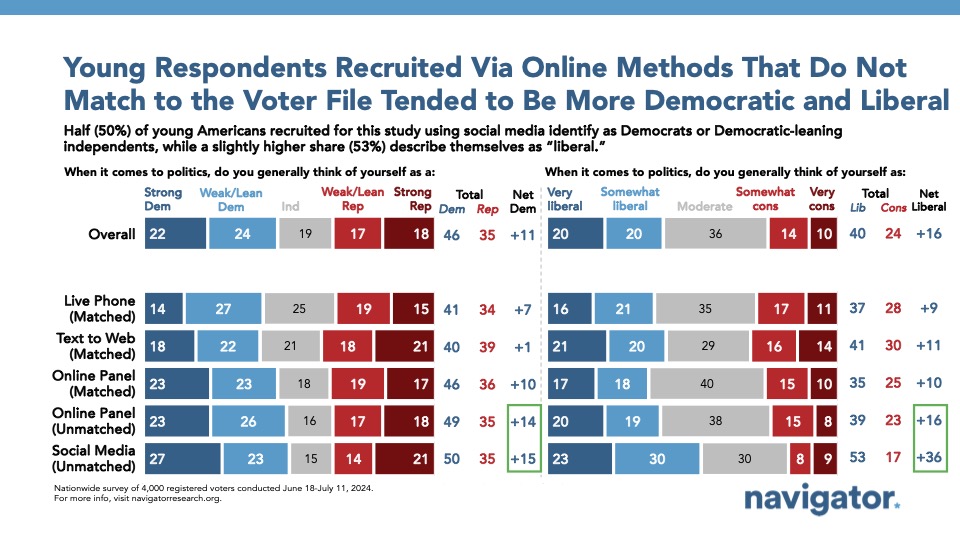
Respondents recruited by online panel and social media platforms tended to identify as more Democratic.
Younger Americans who completed this survey by live phone and text to web were slightly more Republican and conservative than those who completed it by online panel or in-platform social media recruitment. After weighting each mode and the full dataset to the population of national registered younger Americans, they held an 11-point Democratic partisan identification advantage (46 percent Democrats – 35 percent Republicans) and a 15-point liberal ideological advantage (40 percent liberal – 25 percent conservative). Among those taking the survey by live phone, they were only 7 points more Democratic in partisan identification (41 percent Democrats – 34 percent Republicans) and 9 points more liberal (37 percent liberal – 28 percent conservative); text to web respondents were even more split on partisan identification (40 percent Democrats – 39 percent Republicans) but identified as liberal by a double-digit margin (41 percent liberal – 30 percent conservative).
In-platform social media recruitment recruited younger Americans that were more Democratic-identifying by 15 points (50 percent Democrats – 35 percent Republicans) and identified as 36 points more liberal than conservative (53 percent liberal – 17 percent conservative).
Online panel interviews that were not matched to a voter file were also much more Democratic in partisan identification (by 14 points) and more liberal in ideological identification (by 16 points), but online panels that were matched to a voter file were much closer to mirroring the partisan identification and liberal affiliation as the complete dataset of younger Americans (more Democratic by 10 points and more liberal by 10 points).
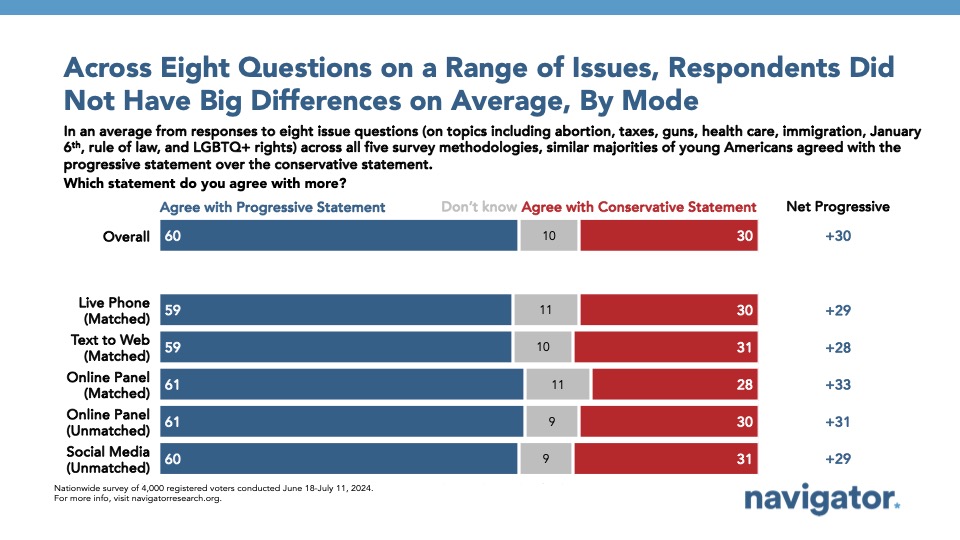
However, when it comes to issue positions, younger Americans hold similar issue attitudes despite differences in which mode they participated in this survey.
Our last report showed that the share of younger Americans who on average agree with the progressive statement on a number of issues was 60 percent, 29 points higher than the share who agree on average with the more conservative position on issues (31 percent). These margins are fairly consistent across mode, including a 33-point progressive advantage among those who took the survey by matched online panel, a 31-point progressive advantage among both unmatched online panel and in-platform social media recruitment, a 29-point progressive advantage among those completing the survey on live phone, and a 28-point progressive advantage among those taking the survey by text to web.
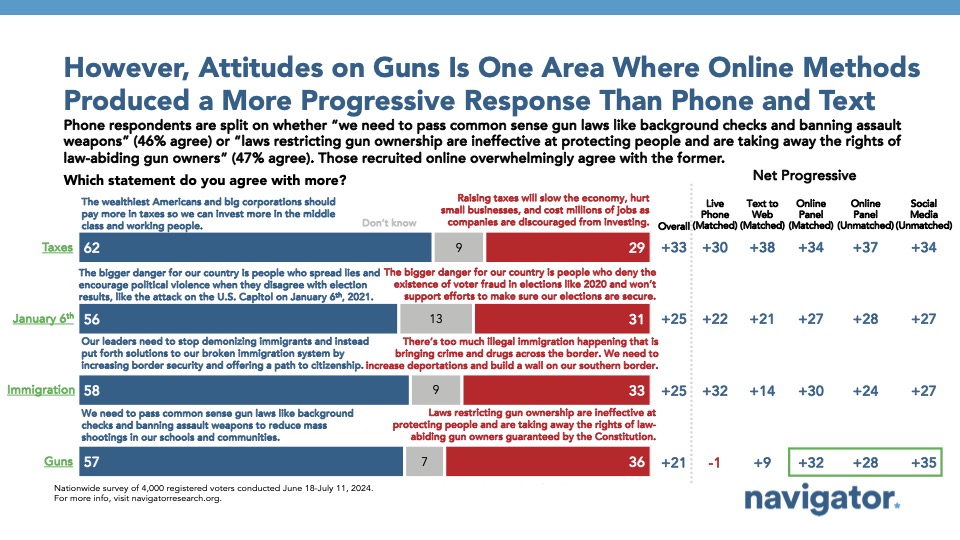
One notable issue in which there were observable differences was on the issue of stronger gun laws. Among all younger Americans, more side with the position that “we need to pass common sense gun laws like background checks and banning assault weapons” than the conservative position that “laws restricting gun ownership are ineffective at protecting people and are taking away the rights of law-abiding gun owners” by 21 points (57 percent progressive position – 36 percent conservative position). Those taking the survey on live phone were significantly more split on this question (net -1; 46 percent progressive position – 47 percent conservative position) as were those who took the survey via text to web (net +9; 52 percent progressive position – 43 percent conservative position). Other modes yielded more agreeing with the more progressive position on guns, including by in-platform social media recruitment (net +35; 65 percent progressive position – 30 percent conservative position), matched online panel (net +32; 62 percent progressive position – 30 percent conservative position), and unmatched online panel (net +28; 60 percent progressive position – 32 percent conservative position).
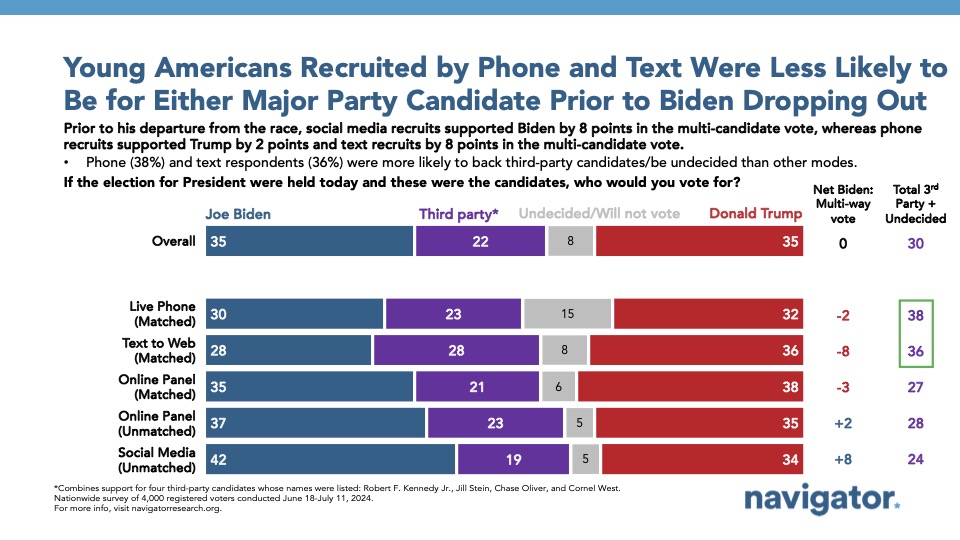
There were observable modal differences in attitudes about the 2024 presidential election, political participation, and the economy.
Modal divergence between phone and text to web interviews versus online panel and in-platform social media recruitment interviews was strongest when assessing the 2024 presidential election, the state of the economy, and self-reported political engagement. This survey — which fielded in late June and early July entirely before President Biden declined to run for a second term — asked a multi-candidate vote preference question about this year’s presidential election. Biden and Trump were tied at 35 percent each among all younger Americans completing this survey, with 22 percent reporting voting for a third-party candidate. As live phone and text to web reported more Republican and conservative affiliation, they were also modes where Trump held a narrow lead over Biden among younger Americans (Trump by 2 among live phone respondents; Trump by 8 among text to web respondents). Among in-platform social media recruitment interviews and unmatched online panel interviews, Biden held advantages (by 8 on social media and by 2 for unmatched panel interviews).
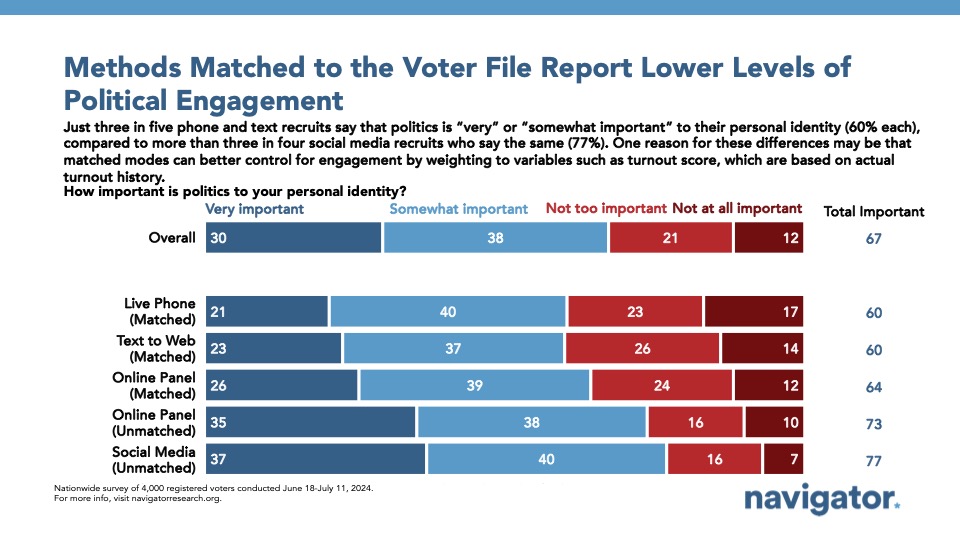
Those completing the survey from social media platforms and unmatched online panel interviews tended to be significantly more likely to consider politics important to their personal identity (77 percent and 73 percent, respectively) than those taking the survey via live phone or text to web (60 percent each).
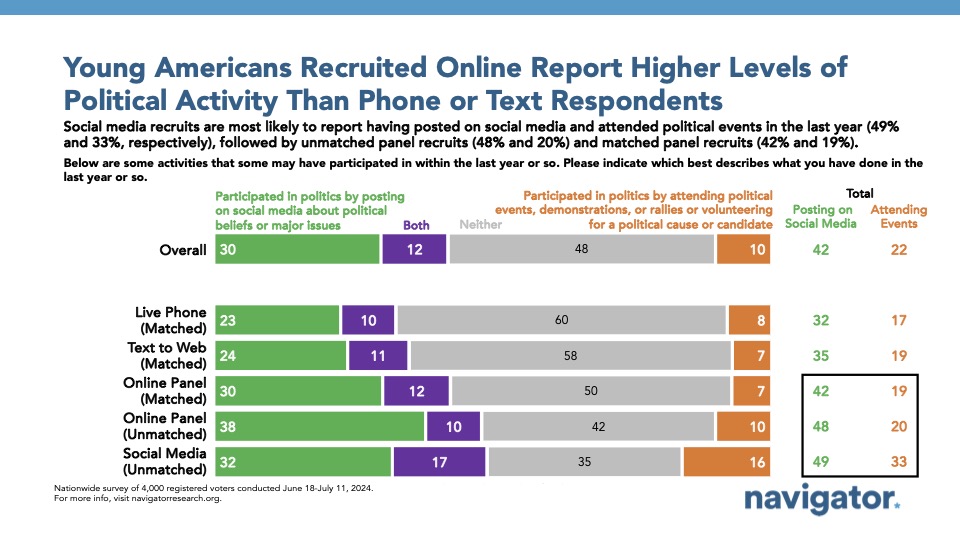
This also transferred into higher levels of self-reporting participation in politics via social media, attending events, or both among those taking the survey via social media (65 percent) or unmatched online panel interviews (58 percent), and lower rates of participation among those taking the survey via text to web (42 percent) or live phone (40 percent).
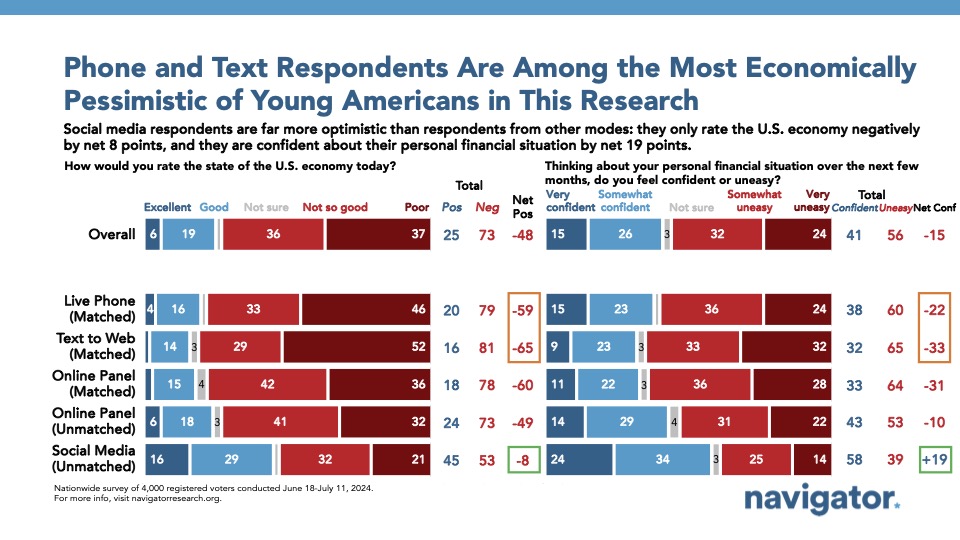
Live phone respondents were also significantly more negative about their perception of the U.S. economy today (net -59) and their personal financial situation (net -22), as were text to web respondents (net -65 on the state of the U.S. economy; net -33 on confidence in their own personal financial situation). By contrast, in-platform social media respondents were significantly more positive: they were only a net 8 points more negative about the state of the nation’s economy (45 percent confident – 53 percent uneasy) and net positive in confidence about their personal financial situations by a net 19 points (58 percent confident – 39 percent uneasy).